Who Coined IOT?
Kevin Ashton – Father of Internet of Things, in short IOT. For Kevin Ashton, the co-founder of Auto-Id Center, back in the year 1999, had decided to find out the holes in data about the supply chain that eventually led him to drive the early deployment of RFID chips on inventory.
Asked by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology to start a group — the Auto-ID Center — that would research RFID technology, he found a way to talk about RFID to a less-than-computer-savvy crowd – by coining the phrase the Internet of Things or IoT.

The Internet of things (IoT) is meant for using the Internet to empower computers to sense the world for themselves.
KEVIN —-
What is IOT?
The Internet of things (IoT) was introduced to remove the gap between the physical and digital world.
IoT connects various things or devices such as home appliances, industrial devices, vehicles, medicinal equipment with computers or smart phones through the internet and therefore turns them into smart devices which can sense and communicate with each other without human intervention.
The sensors on these things gathers data and the IoT platforms analyses the digital data and employs mechanism to help decision makers to implement intelligent and cost-effective solutions on their smart devices or things.
IOT Key Components
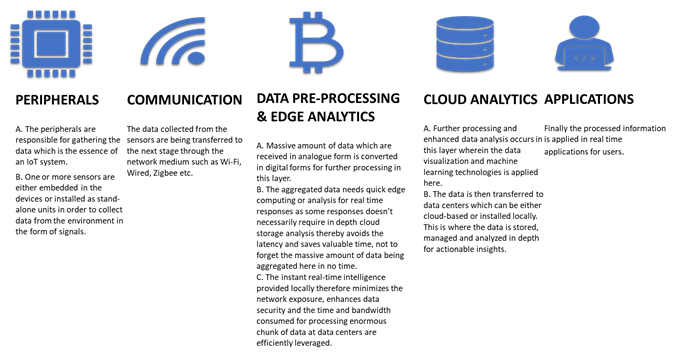
IOT is essentially an interaction between Internet of things and their purpose to make people’s life better in every walk of life. IOT’s primary purpose is to connect machines, people, and data. Then to enable people to machine and machine to machine Interaction.
In, Internet of people, people share/post information with one another that generates a huge chunk of data/information which is being pumped into the cloud.
In, Internet of things, objects/things are pumping data into the cloud which helps in monitoring the product, control, optimize and eventually automate the product on purpose.
As you can see information and data are being shared into the cloud by both people and things. Internet of things can control a product’s behavior and how we can draw value from them.
This categorizes the product into physical components, smart components, and connectivity components, which are most likely to be remotely controlled by an app.
This eventually impacts the product value altogether and thus it impacts the business and people in their day-to-day livelihood.
IOT – Most Popular Use Case
Tesla car utilizes the IOT feature to send their new software features/updates digitally over the internet to their products.
Tesla used the evergreen design strategy to avoid a Major recall.
Few years back when there were several instances in which the battery cell of the car rubbed against the roads as the car turned corners causing fires.

Instead of sending all the Tesla cars back to the dealers or the mechanic shop, the company sent a software update that automatically raised the clearance of the car chassis where the battery was located.

Tesla’s ever green design saved the company money as well as customer’s time and money that usually hurts by a traditional recall of the product.

IOT – Few Challenges
- Handling the huge chunk of data that gets generated from various devices interconnected with each other within the IOT network.
- Complexity of the multiple systems embedded into IOT network and environment setup is complex and costly.
- Too many Networks, protocols, gateways and device hubs is imaginably involved within the IoT network.
- New challenges arise in upgrade testing when different platforms are part of IOT system which could eventually lead to security and compatibility issues.
- Data security and cyber-attacks in today’s evolving times are certainly a challenge.
- Effective maintenance of IOT Test automation framework in a complex embedded system is a challenge on its own.